I have not ever tasted so many interesting flavors in one sitting. There were two kinds of goat, and Egyptian (cookies?) all made from ancient recipes by our amazing contributor Caitlin. We drank pungent Greek red and white wine and feasted on supplementary Greek inspired food including an assortment of baklava, compliments of the lovely Rebecca. It was a fine evening!
Nate and Nialls were missed and we look forward to the next time we will all be at a salon together.
In our first discussion We aspired to start at a beginning. In our second meeting we found that setting a date range only led us to find that there is not a true definitive starting point. We asked aloud "What defines a civilization?" We can not tell when it began if we don't know what we are looking for. After some discussion we came up with several qualifiers: non nomadic, systematization of labor, agriculture and architecture.
Minutes from 2000-0BCE
Joanna, "The History of History"
3200-2600 BCE coherent text, historic text.
In Italy- the Italic alphabet. Roman play write Plautus in 250BCE wrote the earliest of Latin literature.
In Germanic territories earliest manuscripts 200-750 AD.
Neolithic Period 9500-BCE
Bronze Age 3350BCE
Earliest writings were found 4000 BCE "protowriting" a symbol system.
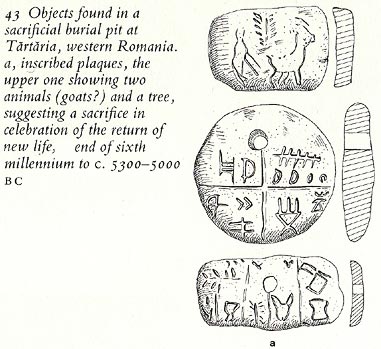
5000 BCE Tartaria tablets in Romania (Image)
Distillia Tablets, earliest in the world, from 5020 BCE.
6000 BCE archeologists have found tortoise shells from China with Jiahu script, considered incoherent text. Bronze Age Protowritig
3100-1200 BCE Near East
3000-600 BCE Europe
Sumer in 2000 BCE Cuniform script. Use of a blunt Reed to make markings.

Iron Age: Neo-Assyrian Empire 934-609 BCE
Alphabet replaces cuneiform. In Mesopotamia, the cradle of civilization. The first real empire of human history. Aramaic: Official Language. Alphabet adopted from Phoenician. All Middle East language can be traced back to Aramaic: Christian, Buddhist and Islamic.
Part II
Cass, Egypt/Communication
Early Dynastic Period3150-2686 BCE 0-II dynasties
Narmer is the first king and unites Upper and Lower Egypt.
The Old Kingdom 2686-2181 BCE III-VI
Zoser builds step Pyramid,
Pharaoh Khufu bulids Great Pyramid,
Pharaoh Khephren has Great Sphinx carved.
The First Intermediate Period 2181-2040 BCE
Anarchy and Chaos
Middle Kingdom 2040-1780 XII dynasty
Pharaoh restores order to the land
The Second Intermediate Period 1780-1570 BCE
Period of weak rulers and invasion by the Hyskos who ruled the North.
The New Kingdom 1570-1070 BCE
The Golden Age
Dynasty XVIII
1570-1546 BCE- Ahmose I, Hyskos are expelled from Egypt
1551-1386 BCE Pharaohs Tuthmosis III, Hatshepsut and Amenhotep III increase power
and wealth of Egypt
1386-1349 BCE Amenhotep III
1350-1334 BCE Amenhotep IV aka Akhenaten
1336-1334 BCE Smenkare
2000 BCE Akkadian/Sumerian
Historians do not agree on whether or not one culture created writing. Our understanding of the history of writing is based on studies of clay tablets and other organic materials that are preserved for a variety of reasons. It is essential to imagine that earlier records could have existed.
Hieroglyphics: From the Greek word hieroglyphikos (sacred carvings) a system that utilizes pictograms to represent complete words, syllables or sounds.Tokens, ceramic pieces in varying geometric shapes, were an ancient instrument of communication used for reading and mathematics. Stones that were shaped like an Egyptian scarabs would be marked with hieroglyphics with a message from the Pharaoh and sent out as if it were a telegram to people of Egypt or to a neighboring land owing dues to Egypt.
In early kingdoms the rise of power was accomplished through the development of communication.

